Structured VS Unstructured Data: A Comprehensive Guide
Data is the foundation of every modern organization, powering growth, decision-making, and competitive advantages. But not all data is the same. Businesses must tackle two primary types of data, each with their own unique challenges and opportunities. Understanding the differences between structured vs unstructured data is crucial for managing resources effectively. With unstructured data making up around 80% of all enterprise information, mastering its management can put your business ahead.
This guide dives into what structured and unstructured data are, their similarities, differences, and how to handle them to unlock their full potential.
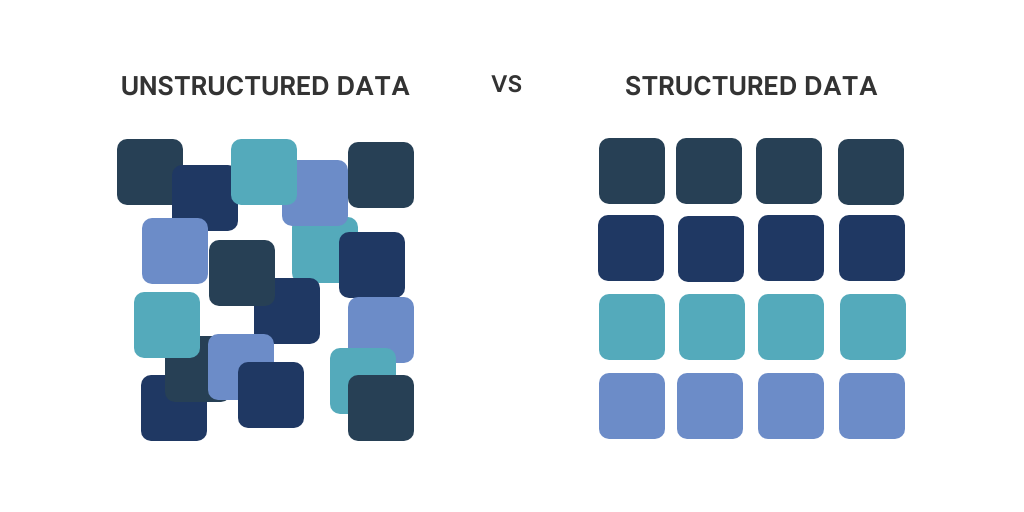
What is Structured Data?
Structured data is the most familiar type of data for most businesses. It is highly organized and formatted to fit into predefined models, such as spreadsheets or relational databases. This type of data works perfectly with traditional storage and management tools, making it easy to analyze and interpret.
Key Characteristics of Structured Data:
- Organized Format: Data is neatly stored in fixed rows and columns, often with clear labels or identifiers.
- Machine-Searchable: Search tools and algorithms can analyze structured data quickly and efficiently.
- Quantitative Focus: Structured data is largely numeric or categorical, used for tasks requiring precision.
Examples of Structured Data:
- Contact information such as names, email addresses, and phone numbers.
- Financial data, including transactions, sales records, and budget metrics.
- CRM data like customer purchase history, demographics, or loyalty points.
Use Cases for Structured Data:
Structured data is ideal for tasks that require consistency, accuracy, and speed. For instance:
- Managing financial reporting and compliance.
- Powering enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems or inventory management platforms.
- Monitoring real-time metrics, such as website traffic or order fulfillment.
By providing easily accessible insights, structured data empowers businesses to perform analytical tasks with precision.
What is Unstructured Data?
Unstructured data on the other hand is fundamentally different from structured data. It doesn’t follow specific formatting rules or fit neatly into rows, columns, or predefined databases. Instead, it exists in its raw form—text documents, multimedia files, or social media posts, for example. This data is harder to process but contains some of the richest and most valuable insights for organizations that can harness unstructured data properly.
Key Characteristics of Unstructured Data:
- Unorganized and Diverse: Unstructured data lacks a fixed schema or organization.
- Requires Advanced Tools: Machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) are essential for processing large bodies of unstructured data.
- Qualitative Content: Often narrative or multimedia, offering subjective insights.
Examples of Unstructured Data:
- Word documents, PDFs, and PowerPoint presentations.
- Audio files from meetings, calls, or podcasts, as well as video content.
- Emails, chat messages, and social media posts or comments.
Use Cases for Unstructured Data:
Unstructured data holds enormous untapped potential across various industries:
- Customer Insights: Sentiment analysis of social media or customer feedback.
- Risk Assessment: Analyzing internal communications for compliance flags.
- Marketing Strategy: Understanding audience behavior through logs, comments, and posted media.
Without proper strategies and tools, this valuable data often goes unused, missing critical opportunities for growth and innovation.
Semi-Structured Data Explained
Semi-structured data bridges the gap between structured and unstructured data. It doesn’t conform to rigid structures but includes metadata or tags that hint at how it can be organized. Semi-structured data often has elements of both types, making it more flexible and versatile.
Key Examples of Semi-Structured Data:
- Extensible markup language (XML) and JavaScript Object Notation (JSON).
- IoT (Internet of Things) data, blending numeric readings with unstructured logs.
- Emails with structured headers (e.g., sender, recipient, subject) but unstructured bodies.
Semi-structured data is particularly useful for industries like eCommerce, where metadata helps categorize vast product inventories or personalize user experiences.
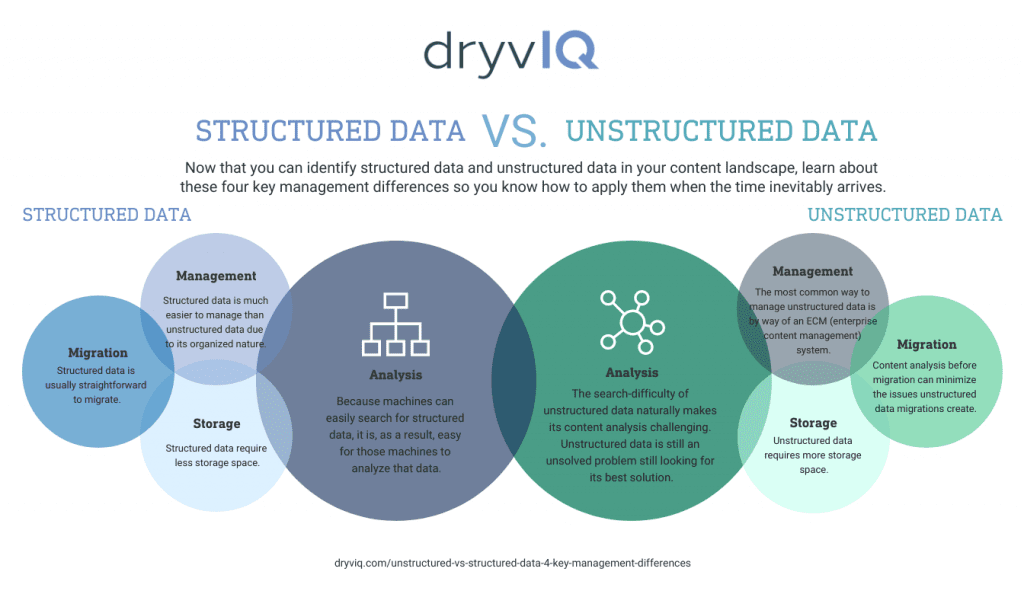
Structured vs Unstructured Data Management Differences
Successfully managing structured vs unstructured data requires tailored approaches. They differ in areas such as analysis, storage, and migration, which must be addressed to unlock the full power of both.
1. Analysis
How Structured Data Is Analyzed:
Structured data is the easiest to analyze because of its organized nature. Tools like SQL databases make it straightforward to extract metrics, identify trends, or answer specific queries. Businesses often rely on structured data for activities such as forecasting, reporting, and compliance.
How Unstructured Data Is Analyzed:
Unstructured data requires advanced AI and machine learning capabilities. These tools use natural language processing (NLP), pattern recognition, and contextual learning to derive meaning from disparate and seemingly chaotic data.
Example Use Cases:
- Structured Data Analysis: Running a report on monthly sales by region.
- Unstructured Data Analysis: Evaluating customer opinions about a product by analyzing online reviews.
The ability to analyze unstructured data can give businesses a significant competitive edge by uncovering hidden insights.
2. Management
Structured data is easier to manage because of its predictability. It can be stored, organized, and accessed using relational databases and traditional ECM systems. Unstructured data, on the other hand, demands more sophisticated tools and strategies.
Best Practices for Unstructured Data Management:
- Leverage enterprise content management systems to centralize storage.
- Automate classification processes using AI to reduce inefficiencies and errors.
- Tag sensitive information to maintain compliance with regulatory standards, like GDPR or HIPAA.
Management of unstructured data isn’t just an operational necessity; it’s vital for minimizing exposure to compliance risks and maximizing productivity.
3. Storage
Storage needs differ drastically for structured vs unstructured data. Structured data typically resides in relational databases or data warehouses. Unstructured data is far larger in volume and diversity, requiring more scalable solutions like data lakes or object storage systems.
Storage Solutions:
- Structured Data: Use relational database systems like MySQL to store highly organized content.
- Unstructured Data: Employ cloud-based storage, NoSQL databases, or Hadoop-based systems for flexibility and scalability.
By 2025, unstructured data is expected to grow to a staggering 175 zettabytes globally. Businesses must ensure their storage solutions can scale while protecting against risks like data breaches.
4. Migration
When it comes to data migration, structured data is typically straightforward, moving cleanly between systems due to its predictable format. Unstructured data migrations, however, are far more challenging due to the lack of organization and the potential inclusion of sensitive information.
Best Practices for Unstructured Data Migration:
- Conduct a thorough content audit to categorize and prioritize data before migration.
- Use AI tools to flag high-risk content, ensuring it’s treated with care during the process.
- Invest in compatible migration tools to ensure file integrity across platforms.
Migration provides an opportunity to optimize your content landscape. Instead of simply moving files, businesses can clean up redundant or irrelevant data, reducing storage costs and improving efficiency.
Why Understanding Structured vs Unstructured Data Matters
Data is a goldmine for businesses, but only if they know how to use it. By managing structured vs unstructured data effectively, companies can realize immense benefits:
- Deeper Customer Insights: Understanding unstructured feedback allows for personalized products and services.
- Enhanced Security: Mitigating the risks associated with unstructured data prevents compliance violations or breaches.
- Smarter Decision-Making: Combining structured metrics with qualitative trends uncovers holistic opportunities for growth.
Many businesses don’t fully utilize their unstructured data, leaving valuable opportunities on the table. With the right tools and strategies in place, organizations can transform these challenges into assets.
Structured vs Unstructured Data: 4 Key Differences Infographic
Make Data Work for You
The debate isn’t about whether structured or unstructured data is better. Each plays a pivotal role in business success depending on the application. Together, they form the DNA of intelligent, data-driven strategies.
Unlocking the potential of your data provides tangible results—from streamlined operations to market leadership.
Contact DryvIQ today to discover how you can gain complete visibility into both structured and unstructured data and revolutionize the way your organization operates.
